Plastic surgery of the anterior cruciate ligament
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is a ligament responsible for the stability of the knee joint, connecting the bones of the tibia with the femur.
Knee injuries are most often associated with damage to the anterior cruciate ligament. Treatment of such injuries is usually carried out surgically, including anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction (ACL reconstruction).
Plastics of the chemical industry
- is an arthroscopic intervention aimed at removing the damaged ligament and replacing it with a graft. This procedure is also known as transplantation or reconstruction. If the operation is performed properly, the functionality of the joint is fully restored.
To replace the ligament, the patient's own tendons are used, usually the semitendinosus muscle or the vastus medialis muscle. The use of these tissues ensures minimal disruption of knee joint function, minimizes cosmetic defects, and facilitates faster rehabilitation.
The operation is performed by arthroscopy, a high-precision surgical intervention that avoids damage to soft tissues, nerves and blood vessels. All manipulations are performed in the area of the injury, which eliminates the formation of noticeable scars or scars.
Anesthesia is used during the procedure. To perform the operation, the surgeon makes several small punctures: one for the optical probe with a video camera (5 mm) and one or two punctures (up to 5 mm) for auxiliary instruments. The arthroscope, which provides 40-60 times magnification of the injury area, allows the intervention to be performed with maximum accuracy.
Indications for surgery:
ineffectiveness of conservative treatment;
frequent repeated injuries;
incorrect transplantation that did not provide stability;
transverse tear of the ligament along its entire width;
complete separation of the fibers from the bone;
significant instability of the knee.
Contraindications to the operation:
restriction of joint mobility;
high risk of complications;
diseases of the cardiovascular or respiratory system;
skin infections, inflammations, pustules, or ulcers;
chronic diseases;
allergic reactions to medications or anesthesia.
Rehabilitation after surgery
During the first month, it is necessary to avoid any load on the injured leg. It is recommended that the patient use crutches to get around. In the first two weeks after the surgery, the patient undergoes physical therapy and physiotherapy under the supervision of a doctor. After about a month, the patient switches from crutches to a cane, and then to walking without additional devices.
Returning to normal life is possible only after the graft is strengthened. Full restoration of joint function usually takes about three months, in some cases up to six months.

Arthrex develops advanced, minimally invasive orthopedic products and surgical techniques that improve the quality of life for people around the world.
Link to the offline site - https://www.arthrex.com/

PCL surgery for torn anterior cruciate ligament 30 years old
The patient, 30 years old, was admitted to the clinic with a diagnosis of anterior cruciate ligament rupture. The tendon of the semitendinosus muscle of the thigh was used as a biological material for the reconstruction of the damaged ligament. Surgery: anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using the Smith & Nephew All-Inside system. After the operation, he was administered ACP (Autologous Conditioned Plasma) - platelet-rich plasma. The method is based on the technology of isolating [...]

ACL surgery Tear of the body and posterior horn of the medial meniscus, tear of the posterior horn of the lateral meniscus 29 years old
A 29-year-old man came to us with a diagnosis: Torn anterior cruciate ligament. Tear of the body and posterior horn of the medial meniscus, tear of the posterior horn of the lateral meniscus. Surgery performed: arthroscopic reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament using the Arthrex ACL All-Inside system and meniscus suture with the Arthrex system. The tendon of the semitendinosus muscle of the thigh was used as a biological material. Full stability of the knee joint according to the [...]
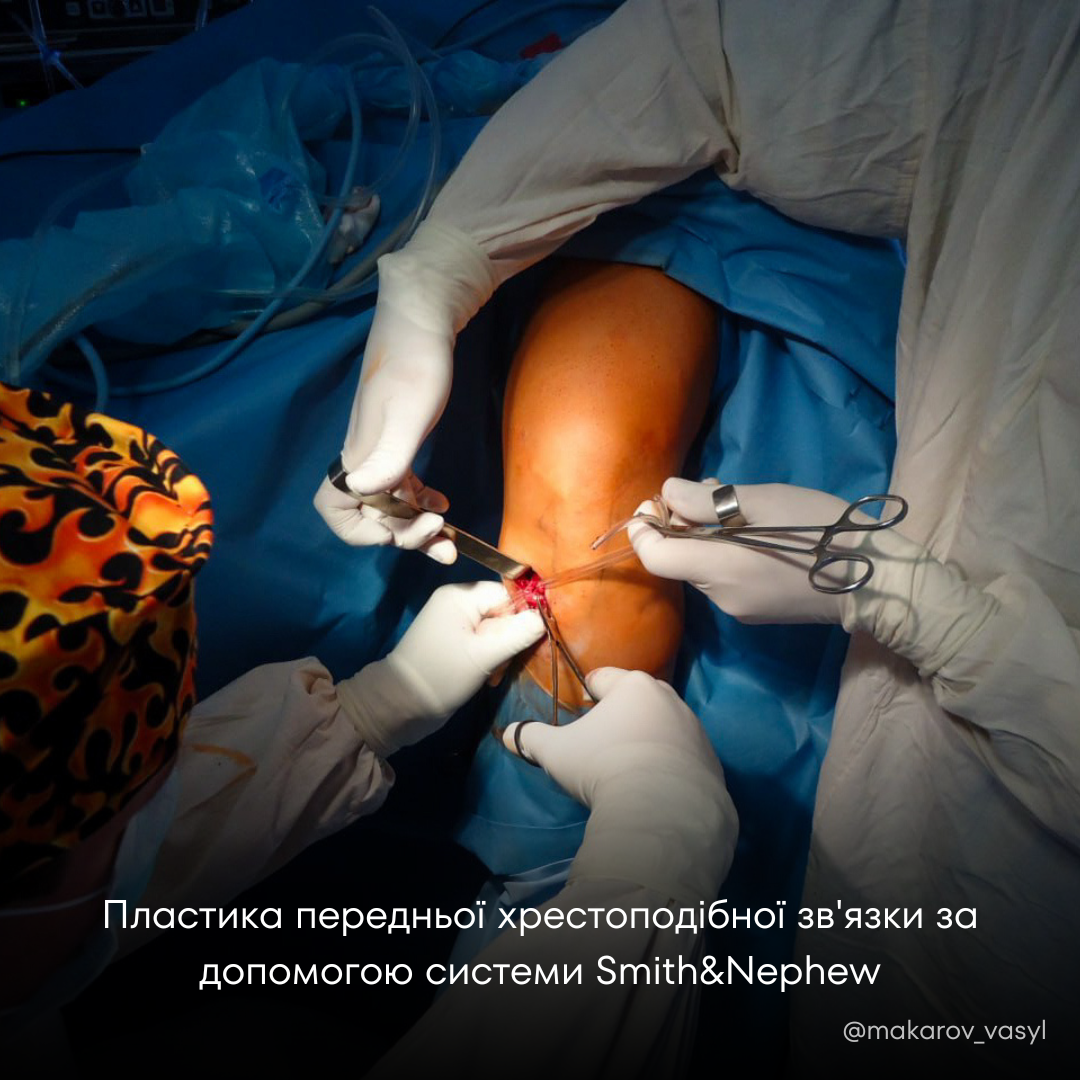
PCL surgery for torn anterior cruciate ligament 30 years old
Patient, 30 years old. Diagnosis: Torn anterior cruciate ligament. The tendon of the semitendinosus muscle of the thigh was used as a biological material for the reconstruction of the damaged ligament. Surgery performed: arthroscopic reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament using the Smith & Nephew system. Fixation of the cruciate ligament implant with a bioreversible endobutton screw. Full stability of the knee joint after the operation.
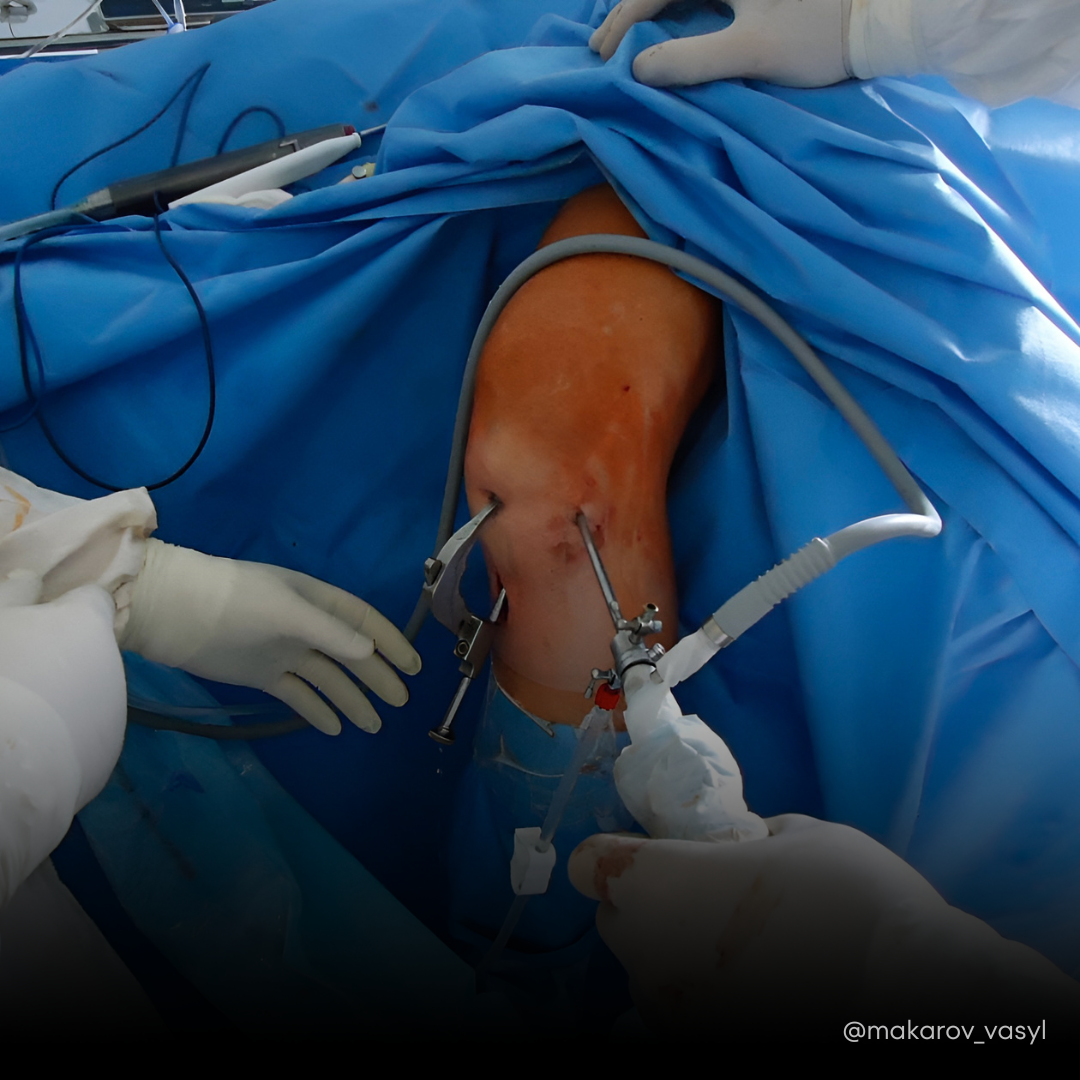
PCL surgery for torn anterior cruciate ligament 28 years old
Male patient, 28 years old, diagnosis: torn anterior cruciate ligament. Surgery performed: arthroscopic reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament using the Arthrex ACL All-Inside system. The tendon of the semitendinosus muscle of the thigh was used as a biological material for the reconstruction of the damaged ligament. After the operation, the knee joint was fully stable. The operation was performed under spinal anesthesia. The postoperative period was uneventful.

PCL surgery for tears of the anterior cruciate and medial collateral ligaments
As a result of an unsuccessful training session, the patient was injured - tears of the anterior cruciate and medial collateral ligaments. He underwent arthroscopy of the knee joint with ACL and MCL reconstruction. The tendon of the semitendinosus muscle of the thigh was used as a biological material for the reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament. Reconstruction of the medial collateral ligament using Fibertape Arthrex. Fixation with two 5 mm bioreposable anchors and [...]
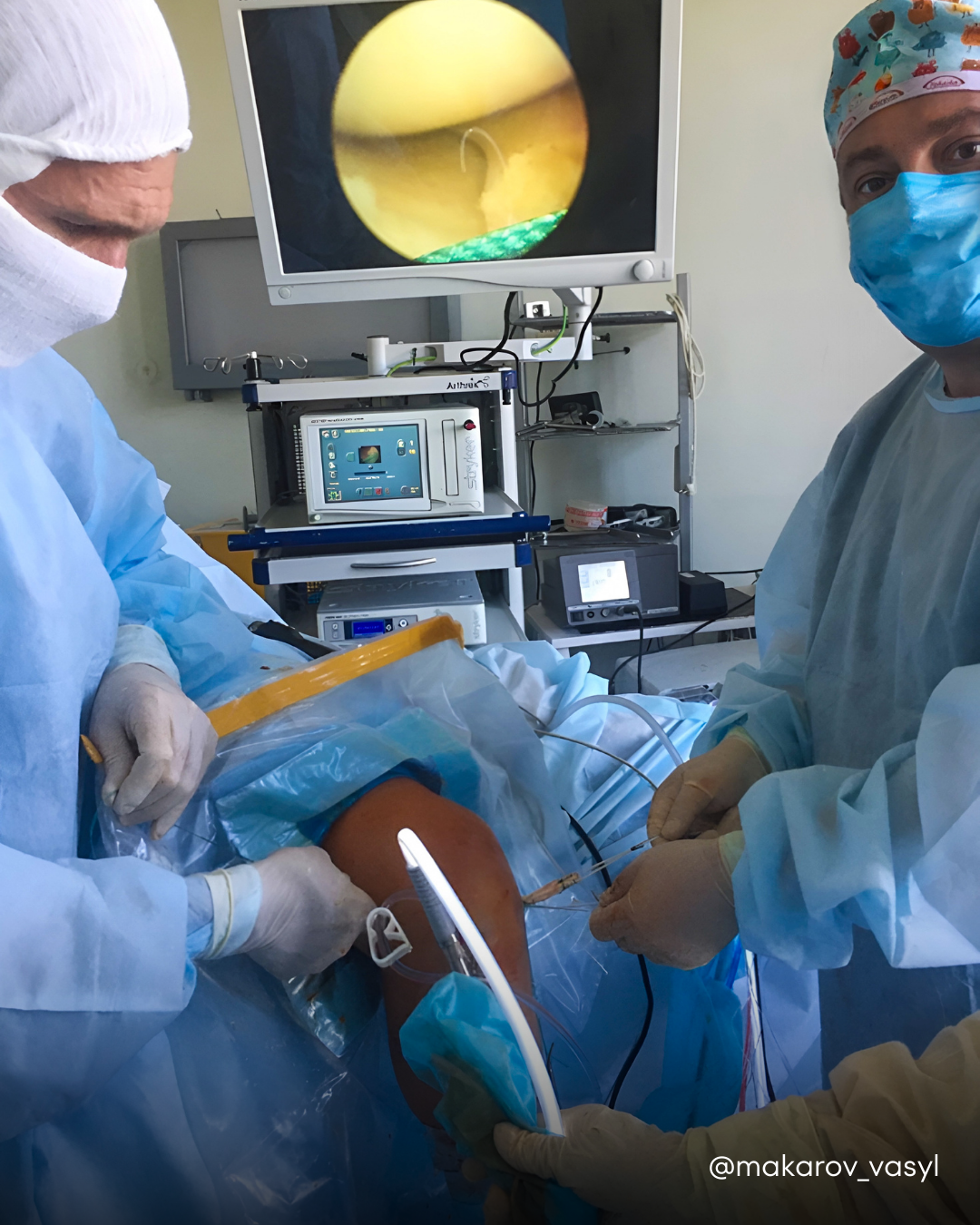
ACL reconstruction tear of the anterior cruciate ligament 32 years old
Male patient, 32 years old, diagnosis: Torn anterior cruciate ligament. Procedure: arthroscopic reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament with the Arthrex All Inside TightRope system. The tendon of the semitendinosus muscle of the thigh was used as a biological material for the reconstruction of the damaged ligament. After the operation, the knee joint is fully stable.